Introduction
As the world moves towards renewable energy sources, wind turbines have become a popular choice for generating electricity. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical power, which is then used to generate electricity. In this article, we will take a look at the mechanics of wind turbines and how they work.
How Wind Turbines Work
Overview of Wind Turbines
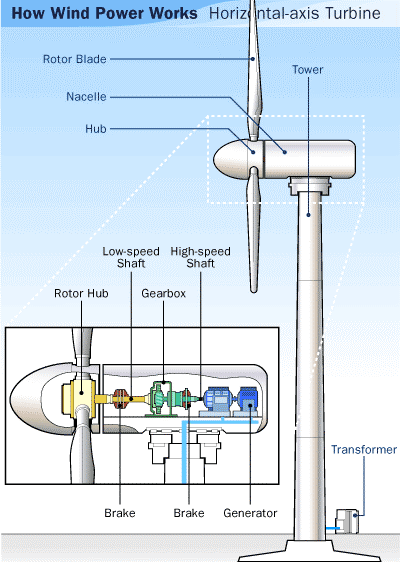
Wind turbines consist of three main components: the rotor blades, the generator, and the control system. The rotor blades are connected to the hub, which is connected to the main shaft. The generator is connected to the main shaft and is responsible for converting the mechanical power into electrical power. The control system manages the speed of the rotor blades to optimize the energy output.
The rotor blades
The rotor blades are designed to capture the kinetic energy from the wind. The blades are typically made from composite materials such as fiberglass and are designed to be aerodynamic to minimize drag. The length and shape of the blades determine the amount of energy that can be captured. The blades are attached to the hub, which is connected to the main shaft.
The Generator
The generator is responsible for converting the mechanical power generated by the rotor blades into electrical power. The generator typically uses an electromagnetic field to induce an electrical current in the wires. The electrical current is then sent to a transformer, which increases the voltage to the level required for the electrical grid.
The Control System
The control system manages the speed of the rotor blades to optimize the energy output. The system uses sensors to measure the wind speed and direction and adjusts the pitch of the blades to maintain a constant speed. The control system also monitors the performance of the turbine and can shut it down in the event of a malfunction.
Wind Turbine Design
There are two main types of wind turbines: horizontal axis and vertical axis. Horizontal-axis wind turbines are the most common and have a rotor that spins horizontally. Vertical-axis wind turbines have a rotor that spins vertically. Both types of turbines have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the specific application.
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines
Horizontal-axis wind turbines have a rotor that spins horizontally and is positioned upwind of the tower. The blades are attached to the hub, which is connected to the main shaft. The generator is located at the base of the tower and is connected to the main shaft. These turbines are more efficient than vertical-axis turbines but are also more complex to design and maintain.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines
Vertical-axis wind turbines have a rotor that spins vertically and is positioned downwind of the tower. The blades are attached to the rotor, which is connected to the main shaft. The generator is also located in the rotor and is connected to the main shaft. These turbines are simpler to design and maintain but are less efficient than horizontal-axis turbines.
Wind turbine efficiency
The efficiency of wind turbines is dependent on a number of factors, including the size and design of the turbine, the wind speed and direction, and the air density. The power output of a wind turbine is proportional to the cube of the wind speed, so a small increase in wind speed can have a significant impact on the energy output. The efficiency of a wind turbine is also affected by the turbulence of the wind, which can cause the rotor blades to stall.
Wind turbine maintenance
Wind turbines require regular maintenance to ensure they continue to operate efficiently. The blades need to be inspected and cleaned regularly to ensure they are free from debris and damage. The generator and control system also require regular maintenance to ensure they are operating correctly. Regular maintenance can help prevent costly repairs and downtime, ensuring the wind turbine continues to generate electricity efficiently.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Turbines
Wind turbines offer a number of advantages over other forms of electricity generation, including:
- Renewable: Wind energy is renewable and abundant, meaning it can be used as a long-term solution to energy generation.
- Clean: Wind energy is clean and does not produce harmful emissions or pollution.
- Low operating costs: Once a wind turbine is installed, the operating costs are relatively low compared to other forms of electricity generation.
However, there are also some disadvantages to wind turbines, including:
- Noise pollution: Wind turbines can produce significant noise pollution, especially for people living in close proximity.
- Aesthetics: Wind turbines can be considered unsightly and may negatively impact the visual appeal of the surrounding area.
- Bird and bat fatalities: Wind turbines can pose a danger to birds and bats, which can collide with the rotor blades.
Conclusion
Wind turbines are a popular choice for generating electricity as they offer a clean, renewable source of energy. By understanding the mechanics of wind turbines, we can better appreciate their design and operation. While there are advantages and disadvantages to using wind turbines, they offer a promising solution to our growing energy needs.
FAQs
- How tall are wind turbines?
- Wind turbines can range in height from 80 to 500 feet.
- How long do wind turbines last?
- Wind turbines typically have a lifespan of 20 to 25 years.
- How much energy can a wind turbine generate?
- The energy generated by a wind turbine depends on the size and design of the turbine, as well as the wind speed and direction.
- How much do wind turbines cost?
- The cost of a wind turbine can vary depending on its size and design, but it can range from $100,000 to $4 million.
- How many wind turbines are needed to power a home?
- The number of wind turbines needed to power a home depends on the energy requirements of the home and the size of the wind turbines.